Psychology
BackThe psychology department aims for all students to question human behaviour and develop an awe of wonder about the interactions between people. Students should develop an inquisitive nature to finding out the reasons why humans behave in a specific way but also to be confident in evaluating key research so that further developments and knowledge continue. Throughout the course students develop a deeper level of empathy.
Learning Journey
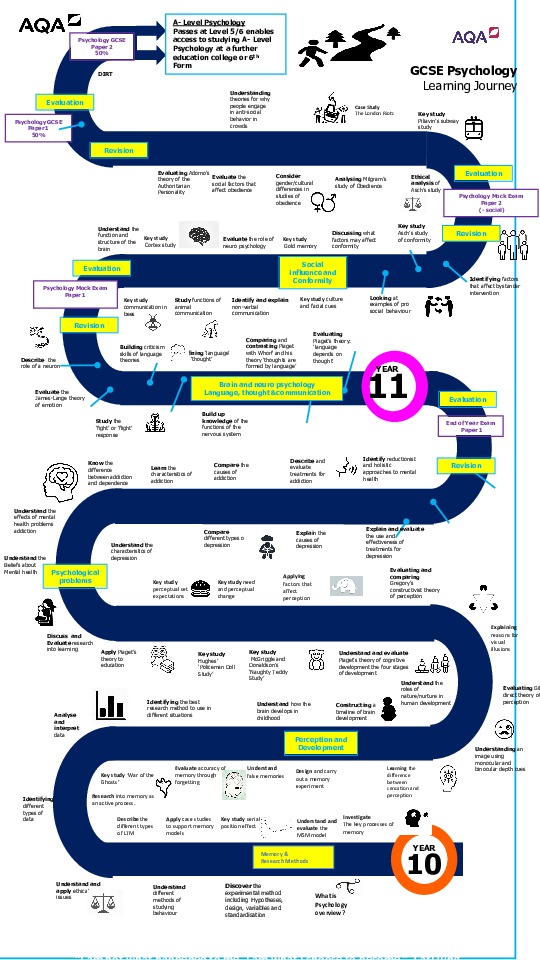
Curriculum Overview
Vision: The psychology department aims for all students to question human behaviour and develop an awe of wonder about the interactions between people. Students should develop an inquisitive nature to finding out the reasons why humans behave in a specific way but also to be confident in evaluating key research so that further developments and knowledge continue. Throughout the course students develop a deeper level of empathy.
In order to be successful Psychology students need to:
- Understand key terminology
- Know how to explain and evaluate theories
- Look at real life behaviours and apply knowledge to explain them
- Have an understanding of key studies and relate to research methods when considering evaluations
| Year 10 | Term 1 | Term 2/3 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | Research Methods | Perception | Psychological problems addiction |
| Knowledge Taught: |
Importance of research Types of data Aims and hypothesis Variables Sampling Experimental method and design Evaluation points for experiments Case studies Correlation Questionnaires Interviews Observations Ethical issues in research Representing data Interpretation of data Reliability and validity |
Differences between sensation and perception Visual cues and constancies Monocular depth cues size, linear perspective, occlusion height in plane Binocular depth cues retinal disparity and convergence Gibson’s direct theory of perception Visual illusions- errors in cognitions Gregory's constructivist theory of perception Factors which affect perception including 1. Culture 2. Emotion 3. Motivation 4. Expectation |
Characteristics of addiction Diagnosing addiction Experimental method Biological theories of addiction Social learning theory Psychological explanations of addiction Treating addiction - aversion therapy Self-management programmes |
| Building from Previous Knowledge: |
Experimental methods Scatter graphs Bar charts Averages Questionnaires |
Visual cues - linear perspective Inferences Schemas Setting out key studies Experimental method - key studies Evaluation of key studies |
Cultural awareness Nature vs nurture Case studies Observations Interviews Questionnaires |
| New Skills: |
Observations -inter observer reliability Carrying out research studies Interpreting results in terms of the hypotheses Sampling Evaluating validity of research method chosen |
Application of depth cues to explaining illusions
Explanation of pictorial stimuli Consideration of how culture influences behaviour Evaluation of theories Debating nature vs nurture |
Consideration of effects on society
Developing empathy through understanding Twin studies Evaluating through reductionism and holism |
| Links to the School Curriculum |
Science - Scientific method of experiments Maths - Representing and analysing data although be aware of the different terminology |
Science - Sensors
Art - Depth cues |
PSHE - Peer pressure
Child development - nature / nurture Science - genetics, hereditary |
| Enrichment Activities |
Design and carry out own questionnaire and collect data Investigate into the Stroop effect |
Assess different types of visual illusions Draw your own visual illusion Rate people’s views on food when hungry or full |
Research into how people are helped to stop addiction. |
| Web Links: | https://www.brainscape.com/flashcards/research-methods-9747963/packs/17311066 | https://www.studysmarter.us/explanations/psychology/cognition/depth-cues-psychology/https://www.youtube.com/watch?app=desktop&v=7GJJXLiN4Ug | https://www.healthline.com/health/addiction |
| Year 10 | Term 1 | Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | Memory | Development | Psychological Problems Depression |
| Knowledge Taught: |
Processes of memory Encoding, storage and retrieval Key study - Baddeley encoding Different types of memory Structure of memory Multistore memory model Key study – Murdock’s serial position curve Memory as an active process Key study – Bartlett’s war of the ghosts Theory of reconstructive memory Factors affecting accuracy of memory Retroactive and proactive interference Context dependent forgetting False memories |
Early brain development Role of nature vs nurture Piaget's theory of cognitive development Schemas, assimilation and accommodation Key developments in stages - conservation and egocentrism Key studies –McGarrigle & Donaldson and Hughes Evaluation of Piaget's theory Application to education Mindset theory of learning Role of praise and self-efficacy Learning styles Willingham’s learning theory Real life application such as learning styles and education. |
Understanding mental health and illness Cultural variations and characteristics of mental health Individual differences in mental health problems Social effects of mental health problems Different types of depression and diagnosis Biological explanations of depression Psychological explanations of depression Treating depression - medication and/or CBT Key study - Wiles assessing effectiveness of CBT Effectiveness of treatments |
| Building from previous knowledge: |
Experimental method Design of study Hypothesis Interpretation of data Calculating averages Drawing line graphs |
Schemas Setting out key studies Observations |
Experimental method Evaluating research studies Schemas Cognitions |
| New Skills: |
Understanding research studies Evaluating research studies Carrying out research studies Evaluating models Application of case studies |
Debating nature v's nurture Evaluating stage theories Evaluating research (Paget’s methods) Application to real world situations - education |
Consideration of effects on society
Developing empathy through understanding Application of treatments from causes Evaluating effectiveness Evaluating through reductionism and holism
|
| Links to the School Curriculum | Whole School - Revision Skills |
Child development - stages of development, Piaget Behaviour 4 learning - Praise and self - efficacy PSHE - self efficacy Science - Parts of the brain |
PSHE - Individual differences
Pastoral - mental health |
| Enrichment Activities |
Test other people on memory studies covered in class. |
Carry out conservation tasks Complete learning styles questionnaire and compare with family members. Check if the results indicate nature or nurture |
Research into the affect COVID 19 has had on the increase on mental health |
| Web Links: | Memory, encoding storage and retrieval | Piaget's Stage Theory | Coping with depression - NHS |
| Year 11 | Term 1/2 | Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | Language thought and communication | Social influence | Revision |
| Knowledge Taught: |
Piaget’s theory and Sapir Wolfs hypothesis on language and thought. Spoken language on recall of events and colours. Animal communication Communication in Bees Form and function of animal and human Communication Verbal and non-verbal communication (Darwin) Factors affecting personal space Nurture / Nature in non-verbal communication Emoticon study
|
Asch's Study on conformity Factors affecting conformity rates such as group size, difficulty, anonymity, personality and expertise. Milgram’s study Factors affecting obedience such as authority, proximity, culture, personality. Milgram’s agency theory |
Application to GCSE questions Focus on command words Addressing importance of key terminology |
| Building from Previous Knowledge: |
Describe and evaluate theories (Piaget) Evidence from Psychology trip (Zoo) Experimental method Application of studies |
Experimental method Predictions of results Criticism of research Cultural evaluations Evaluation of studies including ethics |
All topics covered in past exam papers |
| New Skills: |
Compare and contrast Real life application Animal studies |
Real life experience and application Observation study |
|
| Links to the School Curriculum | Science - Evolutionary Theory |
Science - Scientific method of experiments History - Atrocities due to key authority figures i.e. Hitler |
Relate to what has already been covered. |
| Enrichment Activities |
Watch your pets and observe how they communicate. Watch animals in a park or garden and observe how they communicate |
Carry out Asch’s study on conformity Watch 12 Angry Men Consider how people interact when in pairs or groups |
Looking at past exam papers for Psychology Look at mark schemes and examiner reports |
| Web Links: | https://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=GCSE+psychology+languale+and+communication&docid=607986469785660606&mid=364653D9028936EA513E364653D9028936EA513E&view=detail&FORM=VIREhttps://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=+language+and+communication+in+bees&&view=detail&mid=9C9995C4B487AF31BA349C9995C4B487AF31BA34&&FORM=VRDGAR&ru=%2Fvideos%2Fsearch%3Fq%3D%2Blanguage%2Band%2Bcommunication%2Bin%2Bbees%26FORM%3DHDRSC3 | https://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=gcse+psychology+social+behaviour&ru=%2fvideos%2fsearch%3fq%3dgcse%2bpsychology%2bsocial%2bbehaviour%26FORM%3dHDRSC3&view=detail&mid=B2AD1C8BCD801241909EB2AD1C8BCD801241909E&&FORM=VDRVSR | https://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/psychology/as-and-a-level/psychology-7181-7182/assessment-resources |
| Year 11 | Term 1 | Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | The brain and neuropsychology | Social influence | Revision |
| Knowledge Taught: |
Human nervous system Neuron structure and function Hebb’s theory of learning and neural growth James Lange theory of emotion Brain structure - frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital lobes and cerebellum Localisation of function in the brain Penfield’s study - interpretive cortex Cognitive neuroscience Scanning techniques Tulving’s gold memory study |
Factors affecting bystander behaviour such as presence, cost, similarity and expertise Piliavin’s subway study Collective behaviour factors such as social loafing Crowd behaviour factors such as deindividuation, culture, Personality and morality. Social and dispositional factors
|
See above. |
| Building from Previous Knowledge: |
Early brain development Nonverbal communication CNS and neurons Evaluating theories |
Observation study Learning strategies |
|
| New Skills: |
Localisation Key areas of the brain Medical research and its impact |
Real life application and reporting Observation study Understand the affect others have on our own behaviour |
|
| Links to the School Curriculum | Science - Neurons and CNS |
Sociology - group behaviour Maths - two way tables for observation research |
|
| Enrichment Activities |
Create a model of the brain and identify key areas |
Observe the occurrence of social loafing in group activities Observe behaviour on public transport |
|
| Web Links: | https://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=gcse+psychology+websites+for+the+brain&docid=608002189366067880&mid=44AADEC4C7CA9544DE9344AADEC4C7CA9544DE93&view=detail&FORM=VIREhttps://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=gcse+psychology+websites+for+the+brain&&view=detail&mid=693709B2B3035100CA4D693709B2B3035100CA4D&rvsmid=44AADEC4C7CA9544DE9344AADEC4C7CA9544DE93&FORM=VDRVRV | https://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=gcse+psychology+social+behaviour&ru=%2fvideos%2fsearch%3fq%3dgcse%2bpsychology%2bsocial%2bbehaviour%26FORM%3dHDRSC3&view=detail&mid=A98B5B3ACAA81E822610A98B5B3ACAA81E822610&&FORM=VDRVSR |

