Mathematics
BackMathematics includes the study of number, geometry, algebra and data handling whilst also developing thinking and problem solving skills. In addition to helping you develop good numeracy skills, studying mathematics, even those topics not immediately applicable to real-world situations, will help you develop your ability to think around a problem and find a creative solution.
Learning Journey
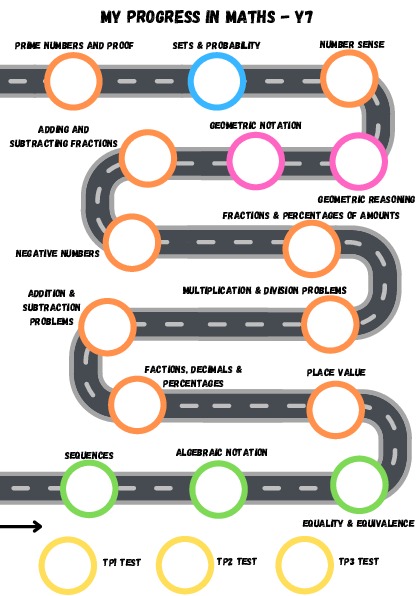
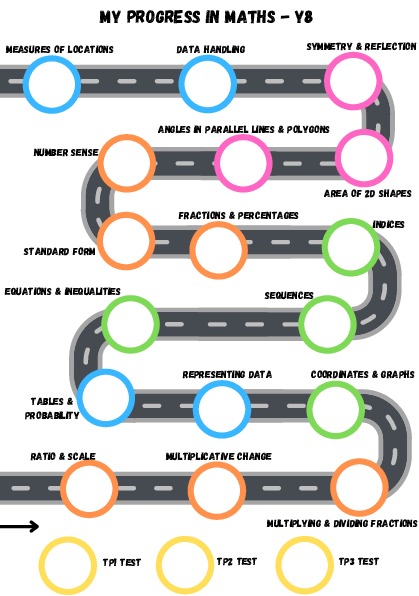
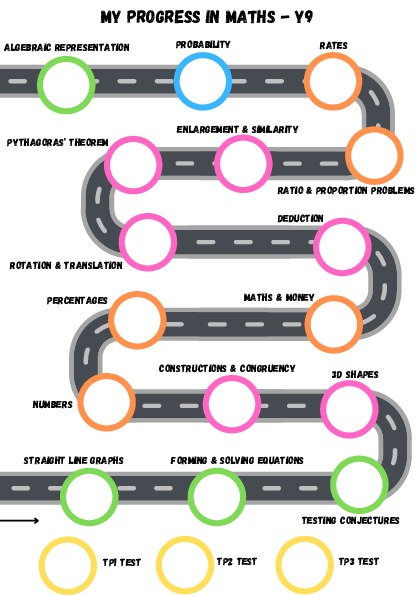
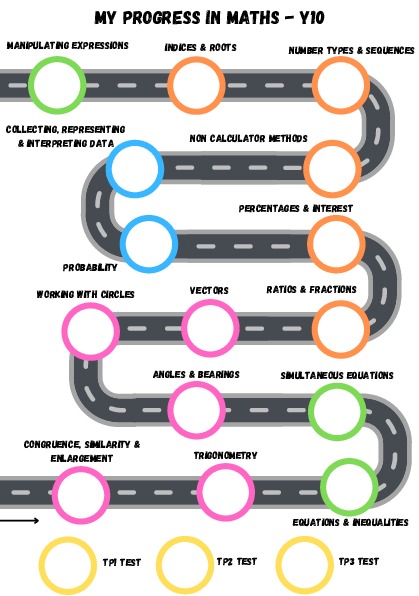
Curriculum Overview
| Year 7 | Term 1 | Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic | Sequences, algebraic notation, place value, fractions, decimals & percentage equivalence | Problem solving with the four operations, fractions & percentages of amounts, negative numbers, adding & subtracting fractions | Constructions, measuring & geometric notation, geometric reasoning, developing number sense, sets & probability, prime numbers & proof |
| New Knowledge |
Linear & non-linear sequences, term to term rules, function machines, substitution, fact families, one-step linear equations, number lines, rounding, finding the range and median, using inequality symbols, fractions on number lines, converting between fractions, percentages & decimals, pie charts |
Financial maths problems, perimeter, tables & timetables, frequency trees, bar charts & line charts, standard form, factors & multiples, multiplying & dividing by a number between 0 – 1, converting metric units, area of rectangles, parallelograms, triangles and trapezia, problems involving the mean, fractions of amounts, negatives on number lines, four operations with negatives, solving two step equations, adding & subtracting fractions, finding equivalent fractions, converting between mixed numbers & improper fractions, adding & subtracting algebraic fractions |
Measuring & drawing angles, 2D shape properties, constructing triangles, draw & interpret pie charts, angles on a point, straight line, in a triangle, quadrilateral & vertically opposite angles, angles in polygons and parallel lines, estimation, mental strategies for the four operations, Venn diagrams, probability vocabulary, sample spaces, probability calculations, prime, triangular & square numbers, HCF, LCM |
| Previous Knowledge Required |
Using the four operations, plotting coordinates, inverse operations, understand a letter as a variable, using a fact family, using a bar model, recognising place value, writing numbers in figures and words, rounding numbers to powers of 10, write a fraction, recognise tenths and hundredths, know that a percentage is out of 100. |
Using the four operations, times tables, inverse operations, knowledge of money equivalence (e.g. £1 = 100p), multiply and divide by 10, 100 or 1000, meaning of a fraction or percentage, equivalence of fractions and percentages, recognise negative numbers, substitution, solving linear equations, order of operations, equivalent fractions. |
Types of angles, using a protractor and ruler, names of 2D shapes, angles on a straight line and in a triangle, using the four operations, times tables, types of numbers (e.g. odd, even, multiples of 10), identify factors, multiples, and prime numbers. |
| New Skills: |
Representing sequences as diagrams, using bar models and part-whole diagrams. |
Reading bank statements, reading a timetable e.g. for a bus, choosing appropriate units. |
Using a protractor, ruler, and compass, draw a Venn diagram and sample space. |
| Links to the School Curriculum: | Percentages link to business, geography and science working out change and yield values. Representing data on graphs and analysing averages and range helps with humanities and sciences where data is used or analysed. Percentages also link to PE and the discussion of VO2 Max/Min and heartrates. | Negative numbers link to temperature in science, and day to day life. They also link to business studies and the pastoral curriculum discussing debt and money. Fractions are an important concept for recipes and cooking in food tech, measuring in product design, science, and economics. | Prime numbers are tied into computer science and security. Constructions and measures form an important foundation for technology and science as well as preparing students for day-to-day life. Probability is strongly linked to business and science predictions/hypotheses |
| Independent Activities: |
M381 M241 M166 M991 M866 M981 M175 M428 M417 M327 M208 M979 M707 M763 M111 M431 M994 M131 M328 M934 M958 M264 M574 M165 |
M901 M920 M635 M690 M460 M738 M140 M183 U280 U211 U751 U529 U236 U739 U250 U993 U970 U226 U934 U945 U575 U424 U265 U343 U904 U881 U916 U291 U947 U325 U704 U736 M601 U685 |
M780 M331 M276 M565 M574 M165 M818 M351 M679 M606 M653 M163 M319 M393 M829 M655 M718 M332 M878 M322 M365 |
| Web Links: |
https://corbettmaths.com/2019/10/07/sequences-nth-term-textbook-exercise/https://corbettmaths.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/forming-expressions-exercise-16-pdf.pdf https://corbettmaths.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/FDP-Key-Equivalents-pdf.pdfhttps://mathsbot.com/gcseMenu |
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zsxhfg8 https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zp26n39https://www.thenational.academy/pupils/lessons/problem-solving-using-all-four-operations-69k32d/overview |
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zs2pdmnchrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://www.okehamptoncollege.devon.sch.uk/uploads/6/1/4/4/61443371/05_year_7_geometric_reasoning_questions.pdf https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/z3x2h4jhttps://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/z3x2h4jhttps://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zytrf82/revision/2 |
| Year 8 | Term 1 | Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: |
Ratio & scale, multiplicative change, multiplying and dividing fractions, 2D coordinates, data representation, probability |
Brackets, equations & inequalities, sequences, indices, fractions & percentages, index form, number sense |
Angles in parallel lines & polygons, area of trapezia & circles, symmetry & reflection, data handling cycle, mean, median, mode & range |
| New Knowledge: | Understanding & representing ratio, solving ratios, dividing in given ratios, comparing ratios and fractions, direct proportion, conversion graphs, similar shapes & scale factors, scale diagrams, multiplying, dividing proper fractions, mixed numbers, improper fractions & algebraic fractions, straight line equations, exploring non-linear graphs, finding the midpoint of a line segment, drawing and interpreting scatter graphs, understanding and describing correlation, lines of best fit, grouped ungrouped frequency tables, two way tables, probabilities from sample spaces, Venn diagrams & using the product rule. | Forming algebraic expressions, expanding & factorising single brackets, solving equations involving brackets, forming and solving simple inequalities, solving equations & inequalities with unknowns on both sides, generating sequences, manipulating expressions with indices, addition law for indices, converting between decimals & percentages greater than 100%, percentage increase & decrease using multipliers, express one number as a fraction / percentage of another, percentage change, calculate with standard form, estimation, problem solving with money, time, and the calendar. | Solving angle problems in parallel lines, sum of exterior / interior angles of any polygon, area and perimeter of compound shapes, circle parts, area of a circle, reflecting shapes in horizontal / vertical / diagonal lines, design and criticise questionnaires, multiple bar charts, choose the most appropriate diagram for a set of data, find the range, compare distributions using charts, identify misleading graphs, choose the most appropriate average, find the mean from an ungrouped frequency table, identify outliers. |
| Previous Knowledge Required: | Multiplication and division, common factors, finding coordinates, using a ruler, writing a fraction, converting mixed numbers and improper fractions, direct proportion, sequences, averages, two-way tables, experiments, events, outcomes, finding probability, Venn diagrams. | Use algebraic notation, simplify algebraic expressions, use negative numbers, substitution, solve one- and two-step equations, form a sequence given the term-to-term rule, calculating with indices, convert key fractions, decimals and percentages, calculate fractions and percentages of amounts with and without a calculator, multiply and divide by powers of 10, rounding to powers of 10 or 1 significant figure, use the order of operations. |
Use angle notation and basic angle rules, construct triangles, find the area of triangles, rectangles and parallelograms, line symmetry, use pictograms, bar charts and vertical line charts, use pie charts, find averages. |
| New Skills | Using a bar model for ratio, drawing a scale diagram, drawing frequency tables and two-way tables. | Using a calculator to work out percentages. | Drawing statistical diagrams. |
| Links to the School Curriculum: | Ratio and scale are essential for map reading in geography, scaling recipes in food tech and underpin key concepts in science. This includes; magnification in biology (microscopes), scale in chemistry for atoms and ratios in reactions and dealing with astronomical scales in physics. Multiplicative change involves the discussion of currency conversions which cross over with the MFL department and potential trips abroad. | Index form is a necessary mathematical notation for studying microscopic organisms/atoms and galactic scale distances such as light years and the speed of light. Percentages are essential for studying profit/loss in economics and business, general financial decisions/investments such as interest rates and yields in chemistry/physics. Algebraic manipulation also underpins many computer programming languages utilised in computer science. | Angles, polygons, and area knowledge are useful when studying tech and product to ensure accuracy in a practical setting. They can also be used in art when considering perspective and looking at abstract designs. Data handling continues to be important in geography, and other humanities subjects where data is analysed and put forward in arguments. |
| Independent Activities: |
Sparx Topic Lists M885 M801 M525 M267 M478 U551 U578 U630 U110 U475 U224 U544 U538 U692 U457 U824 U741 U315 U669 U667 U933 M769 M596 U128 M441 M127 M899 M718 M829 M419 M834 U369 |
Sparx Topic Lists U179 U365 U755 U325 U870 U505 U599 U509 U759 U738 U145 U337 U747 U133 U213 U530 U662 U235 M264 U349 U161 U264 U290 U102 U225 M627 M515 M747 M681 |
Sparx Topic Lists U826 U427 U226 U934 U604 U950 U221 U373 U799 U911 U363 U557 M450 M328 M940 M127 M287 |
| Web Links: |
https://corbettmaths.com/contents/ https://www.stangroundacademy.org/_site/data/files/documents/2C790A054D660A7538D2EA6EF7DBC535.pdf |
|
|
| Year 9 | Term 1 | Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | Straight line graphs, forming and solving equations, testing conjectures, three dimensional shapes, constructions & congruency | Number types, using percentages, money, deduction, rotation & translation, Pythagoras’ theorem | Enlargement & similarity, ratio & proportion, speed / distance / time, probability, inequalities, graphs |
| New Knowledge |
Parallel lines, y = mx + c, real life graphs, inequalities with negative numbers, equations / inequalities in mathematical contexts, rearranging formulae, creating / testing conjectures, expanding binomials, prism properties, names of 3D shapes, plans / elevations, surface area & volume of cuboids / prisms / cylinders, locus from a point, locus from a straight line, locus equidistance from two points, perpendicular bisectors, angle bisectors, explore congruency. |
Explore number types, problem solving with integers, fractions & decimals, solving reverse percentage problems, problems with bills and bank statements, simple / compound interest, VAT, wages / taxes, exchange rates, angle & algebra problems, order of rotational symmetry, rotating 2D shapes, translating 2D shapes, Pythagoras’ theorem to find hypotenuse and other sides, proof of Pythagoras’ theorem. | Enlarging 2D shapes, fractional scale factors, missing sides & angles, problems with inverse proportion, best buy problems, speed / distance / time problems, distance-time graphs, density / mass / volume problems, rates of change & their units, converting compound units, relative frequency, expected outcomes, independent events, using diagrams to work out probabilities, drawing and interpreting quadratic graphs, interpret reciprocal and piece-wise graphs, representing inequalities. |
| Previous Knowledge Required |
Recognise equations for lines parallel to the axes, encourages students to ask their own questions, a skill which links to science, history, and most humanities subjects. Knowledge of 3D shapes is important in art and the sciences; concepts of volume are also necessary for calculating the flow of rivers in geography. |
Work with directed number, HCF and LCM, calculate with theorem is used in the study of stellar distances and the parsec. It is also important for dealing with triangles in technology and product design. |
Use coordinates, multiplying and dividing, direct understand weather patterns in geography. It is also an important concept for understand risk taking in the pastoral curriculum, as well as investments and financial decisions in economics and business. |
| Links to the School Curriculum: | Number work can occur in a variety of subjects | Coordinates on maps in Geography | Area and volume in D&T |
| Independent Activities: |
M932 M544 M888 M843 M771 M205 M767 M518 M229 M884 M534 M661 M936 M765 M722 M697 M124 M985 M196 M565 M232 M239 M253 |
M619 M958 M264 M553 M235 M437 M905 M476 M533 M528 M139 M290 M910 M881 M502 M541 M780 M331 M818 M163 M351 M679 M319 M606 M393 M677 M480 . |
M178 M377 M324 M885 M801 M267 M525 M543 M478 M681 M551 M581 M247 M221 M772 M530 M761 M774 M728 M465 M865 M206 M718 M829 M419 M834 M299 M572 M332 |
|
Year 10 |
Term 1 | Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Learning + Development | Congruence, similarity & enlargement, trigonometry, equations & inequalities, simultaneous equations | Angles & bearings, circles, vectors, ratio & fractions, percentages & interest, probability | Collecting, representing & interpreting data, non-calculator methods, number types & sequences, indices & roots, manipulating expressions |
| New Knowledge: | Missing angles & sides in similar shapes, area & volume of similar shapes, conditions for congruency in triangles, use trigonometric ratios to find missing sides and angles in right angled triangles, sine rule, cosine rule, 3D trigonometry, ½abSinC for area in triangles, inequalities on number lines, straight line graphs to find solutions to equations, form and solve complex equations and inequalities, solving simultaneous equations by substitution, elimination & graphically, form simultaneous equations. | Understand, represent, measure and read bearings, calculate bearings using angle rules, make scale drawings using bearings, use Pythagoras and Trigonometry to solve bearings problems, circumference of a circle, length of an arc, area of a sector, circle theorems, volume of cylinders / spheres / cones, surface area of cylinders / spheres / cones, represent vectors, multiply / add / subtract vectors, link ratios & graphs, combines sets of ratios, link ratios & algebra, repeated percentage change, problems involving growth and decay, estimate probabilities, find probabilities from frequency trees, calculate independent / dependent probabilities from tree diagrams. | Construct / interpret frequency polygons, primary & secondary data, stem & leaf diagrams, understand extrapolation, cumulative frequency, surds, bounds, limits of accuracy, describe the difference between arithmetic & geometric sequences, special sequences, sequences involving surds, quadratic sequences, laws of indices, power 0 and negative / fractional indices, identities, four operations with complex algebraic fractions, algebraic proof. |
| Previous Knowledge Required | Enlarging a shape by a positive scale factor, finding sides and angles in similar shapes, using Pythagoras’ theorem, forming, and solving one- and two-step equations (including with the unknown on both sides) and inequalities, drawing straight line graphs, using a given equation to find related facts. | Use cardinal directions, use a cale diagrams, parts of a circle, area and volume of similar shapes, simplify a ratio, share in a ratio, compare ratio and fractions, link ratio with graphs and scales, converting fractions, decimals and percentages, calculating percentages, increase and decrease by a percentage, write a percentage, find the original amount after a percentage change, add, subtract and multiply with fractions, finding probabilities, probabilities sum to 1, use a sample space. | Two-way tables, pie charts, finding averages from lists and tables, times-series graphs, scatter graphs and lines of best fit, using the four operations with integers and fractions, rounding to decimal places and significant figures, estimation, factors, multiples, primes, finding the HCF and LCM, nth term of a linear sequence, square and cube numbers, powers of 10/standard form, addition and subtraction rules for indices, simplify algebraic expressions. |
| New Skills |
Writing a geometric proof, labelling a triangle for trigonometry, choosing the correct trigonometry or Pythagoras rule to use, multiplying equations. |
Identify a bearing, identify parts of a circle, identify the necessary circle theorem, choose the correct surface area or volume formula to use, recognise the difference between growth and decay, recognise the difference between independent and dependent events. | Choose an appropriate statistical diagram, recognise types of sequences, write algebraic proofs. |
| Links to the School Curriculum | This half term has strong links to the product design and tech curriculum. With a large focus on shapes, angles, and triangles (the strongest shape), there are a lot of transferable skills and knowledge here. Equations and inequalities form a solid foundation for the GCSE physics curriculum, as well as dealing with empirical formulae in chemistry. |
Angles and bearings carry some transferable skills for the geography curriculum. Vectors form a basis for studying of vector and scalar quantities in the GCSE physics curriculum. Rations and fractions continue to provide support for the GCSE Chemistry curriculum when comparing quantities of chemicals in reactions. This is supported by percentages for yields in experiments, and their links to the business and economics curriculums. |
Methods for recording and interpreting data link to the GCSE Child Development curriculum. This skill is also utilised in geography and the humanities. Number types and sequences are crucial to spot patterns and identify trends, this has applications in physics, economics, and child development. |
| Independent Activities | U605 U283 U545 U627 U319 U967 U170 U164 U450 U952 U591 U592 U509 U759 U738 U145 U337 U747 U133 U760 U757 U547 U836 U875 U137 U269 |
U447 U390 U730 U628 U732 U655 U826 U329 U427 U525 U107 U767 U604 U950 U221 U373 U459 U251 U489 U130 U808 U807 U888 U594 U550 U689 U925 U881 U916 U554 U349 U773 U671 U286 U278 U533 U332 U988 U679 U163 U704 U646 U746 U736 U692 U793 U439 U475 U224 U544 U538 U874 U803 U408 U510 U683 |
U200
|
| Web Links: | Solving one step- equationsSolving equationsForming and solving equationsSimultaneous equations Solving simultaneous equations graphicallyInequalitiesInequalities on graphsQuadratic inequalitiesSimultaneous quadratic equationsCongruent trianglesSimilar shapes - lengthSimilar shapes-area + volumeNegative enlargementHarder graphsSohcahtoaExact trig valuesArea of any triangleSine ruleCosine rule3D pythagoras | AnglesBearingsAngles in polygonsAngles in parallel linesCirclesCircle theoremsProof of circle theoremsColumn vectorsVectorsWriting simplifying ratioSharing between a ratioRatio as a fraction or linear functionWriting fractionsFraction of amountFractions, Decimals and PercentagesFractionsConverting recurring decimals to fractionsPercentagesPercentage changeReverse percentagesRepeated percentage changeProbabilityProbability 2Probability treesConditional probability | Bar chartsStem and leaf diagramsPie chartsFrequency polygonsCumulative FrequencyBox plotsSurdsBounds Quadratic nth termIndicesFurther indicesAlgebraic fractions |
| Year 11 | Term 1 | Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | Gradients & lines, non-linear graphs, real-life graphs, expanding & factorising, changing the subject, functions | Multiplicative reasoning, geometric reasoning, algebraic reasoning, transforming & constructing, listing & describing | Revision and examinations |
| New Knowledge |
Equation of a straight line given one / two points, determine if a point is on a line, equations of perpendicular lines, plotting / reading from quadratic / reciprocal / exponential / cubic graphs, identify & interpret roots / intercepts of quadratic, circle equations, tangent to any curve, direct / inverse proportion graphs, find approximate solutions to equations using graphs, estimate area under a curve, factorising quadratics, solving quadratics, completing the square, using the quadratic formula, changing the subject of a complex formula, solving equations by iteration, use function notation, composite / inverse functions, quadratic inequalities, trigonometric functions. |
Complex direct / inverse proportion equations, calculating with pressure & density, more circle theorems, simultaneous equations with one quadratic, simplifying complex expressions, perform / describe combinations of transformations on shapes, invariant points / lines, solve loci problems, trigonometrical graphs, identify transformations, product rule for counting / organised lists, proof with vectors. | None- revision for summer exams! |
| Previous Knowledge Required |
Plot straight-line graphs, find the equation of a straight-line from the graph, solve linear simultaneous equations graphically, reflect shapes in lines, conversion graphs, use real-life straight-line graphs, expand and simplify single and double brackets, solve linear equations and inequalities, change the subject of a simple formula, use a function machine, substitute into expressions, use trigonometric functions. |
Use scale factors proportion and ratio, angles at a point, on a line, in parallel lines and in polygons, using vectors, use Pythagoras and trigonometry, nth term of a linear and quadratic sequence, solve simultaneous equations, understand line and rotational symmetry, perform and describe reflections, rotations, translations and enlargements, perform constructions with a ruler and compass, sample spaces, probability, two-way tables, plans and elevations, averages, scatter graphs. |
Use coordinates, multiplying and dividing, direct understand weather patterns in geography. It is also an important concept for understand risk taking in the pastoral curriculum, as well as investments and financial decisions in economics and business. |
| New Skills: | Recognise the shapes of distinct types of graphs, | None - revision. | None - revision. |
| Links to the School Curriculum: | Gradients lines and real-life graphs carry several transferable skills for data analysis. The sciences have the strongest links to these topics but their ability to interpret economic graphs/models in business studies and economics are also improved. This also ties into Child Development and expected developmental progress. Changing the subject is particularly useful in biology with various biological reactions needing balancing, alongside chemistry and physics equations. | Geometric reasoning benefits their studies in tech and product design, as well as geography. Multiplicative reasoning is used to develop and understand relationships between variables, commonly seen in the geography, science, and business/economics curriculum. | During this term students develop their revision skills. This provides some cross over into other subjects, particularly the sciences. |
| Independent Activities: |
U789
|
||
| Web Links: | Linear graphsReal graphsCubic and reciprocal graphsHarder graphsExpanding and factorisingExpanding and factorising quadraticsExpanding triple brackets | https://www.mathsgenie.co.uk/gcse.phphttps://corbettmaths.com/https://www.mathsgenie.co.uk/papers.phphttps://www.onmaths.com/mock_exams/?archiveType=predictions | https://www.mathsgenie.co.uk/gcse.phphttps://corbettmaths.com/https://www.mathsgenie.co.uk/papers.phphttps://www.onmaths.com/mock_exams/?archiveType=predictions |

