Computing
BackComputing at Aylesford incorporates information communication technology, digital literacy and computer science. This curriculum helps students acquire skills in computational thinking, problem solving and collaboration, allowing our students to make informed choices in our digital world.
Learning Journey
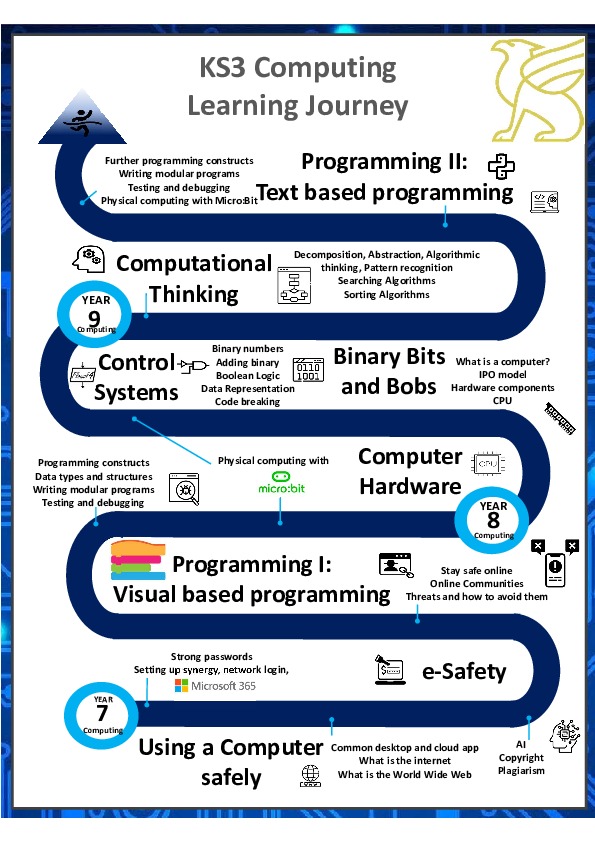
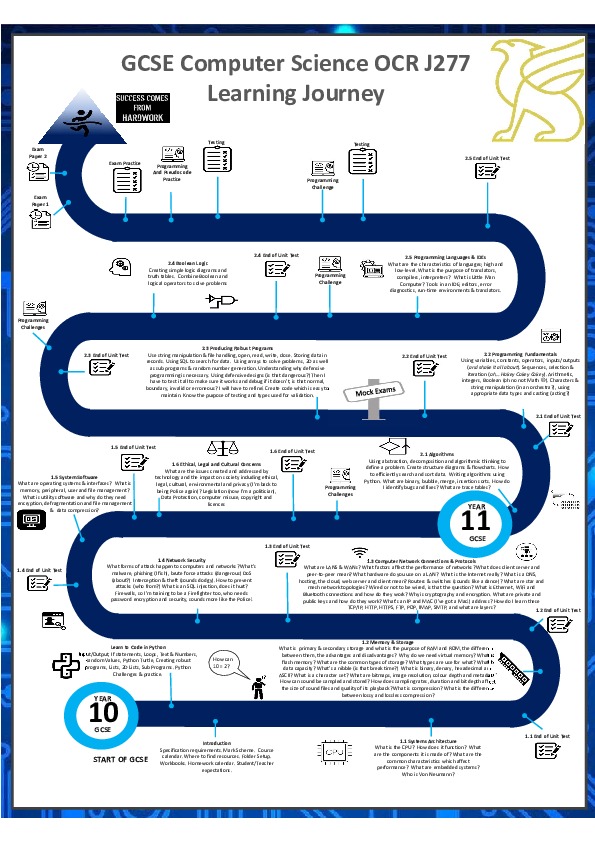
Curriculum Overview
| Year 7 | Topic 1 | Topic 2 | Topic 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | Living in a digital world | e-Safety | Programming I: Visual-based programming with Scratch and Micro:bit |
| New Knowledge: |
|
|
|
| Previous Knowledge Required: | Basic IT skills: using a keyboard, mouse etc. | Basic IT skills: using a keyboard, mouse etc. | Basic IT skills: using a keyboard, mouse etc. |
| New Skills: |
|
|
|
| Links to the School Curriculum: | PSHE – being a responsible digital citizen | ||
| Independent Activities: |
|
|
|
| Web Links: | https://www.typingclub.com/ | https://www.thinkuknow.co.uk/11_18/https://www.blogger.com/https://www.khanacademy.org/computing/hour-of-code/hour-of-code-lessons/hour-of-html/v/making-webpages-intro | https://scratch.mit.edu/https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zhy39j6https://thecrashcourse.com/courses/boolean-logic-logic-gates-crash-course-computer-science-3/https://hourofcode.com/ukhttps://www.101computing.net/category/scratch/ |
| Year 8 | Topic 1 | Topic 2 | Topic 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | Computer Hardware | Binary Bits and Bobs | Control Systems with Flowol and Micro:bit |
| New Knowledge: |
|
|
|
| Previous Knowledge Required: |
|
|
|
| New Skills: |
|
|
|
| Links to the School Curriculum: | Maths: Basic mathematic calculations, operators | ||
| Independent Activities: |
|
|
|
| Web Links: | https://pcbuilder.net/#:~:text=You%20can%20use%20the%20PC%20buildinghttps://www.pcbuildingsim.com/pc-building-simulator#:~:text=Build%20your%20very%20own%20PC%20empire, | https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z9nk87h/revision/1https://thecrashcourse.com/courses/cybersecurity-crash-course-computer-science-31/ | https://www.rigb.org/explore-science/explore/video/hi-tech-trek-chips-everything-2008 |
| Year 9 | Topic 1 | Topic 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: | Computational Thinking | Programming II: Text-based programming with Python and micro:bit |
| New Knowledge: |
|
|
| Previous Knowledge Required: |
|
|
| New Skills: |
|
|
| Links to the School Curriculum: | ||
| Independent Activities: |
|
|
| Web Links: | https://cybergamesuk.com/https://joincyberdiscovery.com/https://bletchleypark.org.uk/ | https://time2code.today/https://makecode.microbit.org/https://www.101computing.net/category/lmc/ |
| Year 10 |
Term 1 |
Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: |
1.1 Systems Architecture and memory 1.2 Data Representation and storage Practical Programming skills |
1.3 Computer Networks, connections and protocols Practical Programming skills |
1.5 Ethical, legal, cultural and environmental Practical Programming skills |
| New Knowledge: |
|
|
|
| Previous Knowledge Required: |
|
|
|
| New Skills: |
|
|
|
| Links to the School Curriculum: |
|
ETHICS: difference between law and ethics | |
| Independent Activities: |
|
|
|
| Web Links: | https://time2code.today/https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zdjfqp3 | https://time2code.today/https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/cloud-systems-management/modeling-labs/index.html#~overview | https://time2code.today/https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/b006m9ry |
| Year 11 |
Term 1 |
Term 2 | Term 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Topic: |
2.1 Algorithms 2.2 Programming fundamentals |
2.3 Logic and Languages |
Revision |
| New Knowledge: |
|
|
|
| Previous Knowledge Required: |
|
|
|
| New Skills: |
|
|
|
| Links to the school curriculum: | MATHS: Calculations, BIDMAS, Floor division |
|
|
| Independent Activities: |
|
|
SMART:REVISE online: https://smartrevise.online/Online revision with interactive questions with Isaac Computing: https://isaaccomputerscience.org/Practise an Algorithm a day: https://revisecs.csuk.io/6-a-day-j276/ Full set of video tutorials: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t8H6-anK0t4&list=PLCiOXwirraUAvkTPDWeeSqAKty3LAG37- |
| Web Links: | https://time2code.today/https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/z7mbxychttps://www.codecademy.com/ | https://time2code.today/ |

